Types of Urinary Incontinence
There are several types of urinary incontinence, including:
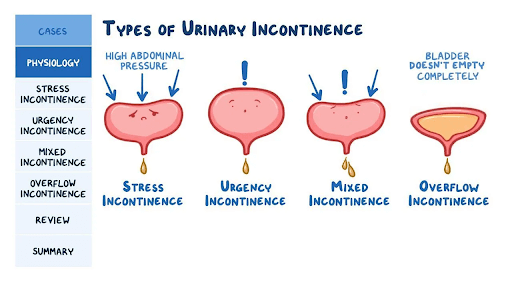
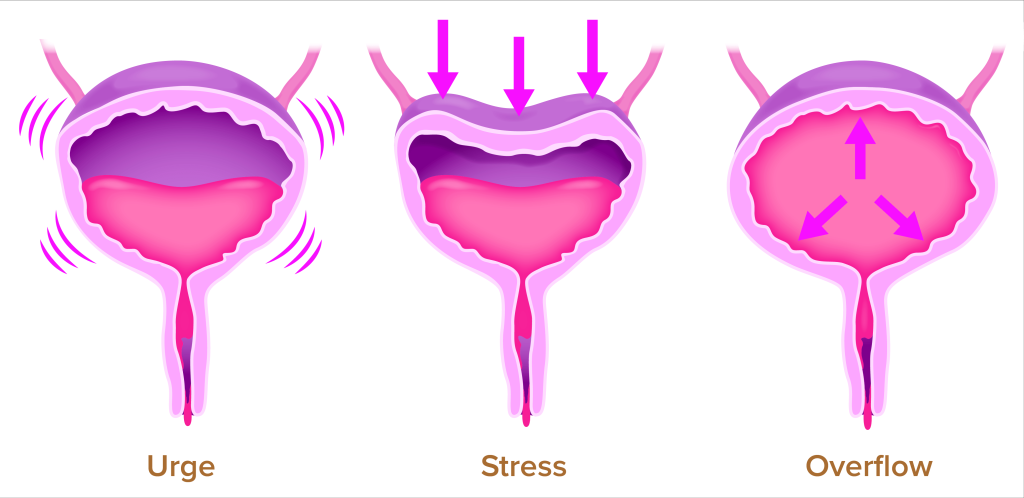
- Stress incontinence: Occurs when there is an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or physical activity, that causes urine to leak out. It is commonly seen in women after pregnancy and childbirth, as well as in men who have had prostate surgery.
- Urge incontinence: Also known as overactive bladder, it is characterized by a sudden and strong urge to urinate, which is difficult to control, resulting in the involuntary loss of urine. It is commonly seen in older adults and can be caused by neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis.
- Overflow incontinence: Occurs when the bladder is unable to empty completely, causing urine to continuously leak out. It is commonly seen in men with an enlarged prostate gland or in individuals with nerve damage that affects bladder function.
- Mixed incontinence: A combination of stress and urge incontinence, where the person experiences symptoms of both types.
- Functional incontinence: Occurs when the person is unable to reach the toilet in time due to physical or mental impairment, such as dementia or arthritis.
Symptoms of Urinary Incontinence
The most common symptom of urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine, but there are other symptoms that may vary depending on the type of urinary incontinence a person is experiencing. These symptoms may include:
- Involuntary loss of urine: Urine leakage that occurs without warning, often during physical activities such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or exercising.
- Strong urge to urinate: A sudden and intense need to urinate, often accompanied by discomfort or pressure in the bladder.
- Frequent urination: Need to urinate more frequently than usual, often more than eight times a day.
- Difficulty starting or maintaining a steady stream of urine: A weak or interrupted urine flow, which may require straining to empty the bladder.
- Bedwetting or nighttime urination: Urine leakage during sleep, which can be a sign of a more severe form of urinary incontinence.
Causes of Urinary Incontinence

Urinary incontinence can be caused by various factors, including:
- Age-related changes: As people age, the muscles and tissues that support the bladder and urethra can weaken, leading to urinary incontinence.
- Pregnancy and childbirth: The pelvic muscles and tissues can become weakened during pregnancy and childbirth, leading to urinary incontinence.
- Menopause: The loss of estrogen during menopause can cause changes in the urinary tract, leading to urinary incontinence.
- Prostate problems: In men, an enlarged prostate gland or prostate cancer can cause urinary incontinence.
- Neurological disorders: Conditions that affect the nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease, can cause urinary incontinence.
- Certain medications: Diuretics, sedatives, and muscle relaxants can all contribute to urinary incontinence.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) or bladder infections: These infections can cause irritation and inflammation in the bladder, leading to urinary incontinence.
- Obesity or being overweight: Excess weight can put pressure on the bladder and pelvic muscles, leading to urinary incontinence.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the muscles and tissues that support the bladder and urethra, leading to urinary incontinence.
Urinary incontinence treatments
Here are some common treatment options for urinary incontinence:
- Behavioral therapies: These can include bladder training, pelvic floor exercises (also known as Kegels), and timed voiding techniques to help improve bladder control.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as anticholinergics, can help calm an overactive bladder and reduce urge incontinence symptoms.
- Medical devices: Pessaries and urethral inserts can help support the bladder and prevent urine leakage.
- Surgery: In severe cases of urinary incontinence, surgery may be necessary to repair or strengthen the muscles and tissues that support the bladder and urethra.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, avoiding bladder irritants such as caffeine and alcohol, and avoiding constipation can all help improve urinary incontinence symptoms.
- Absorbent products: Wearing absorbent pads or disposable underwear can help manage urine leakage and improve quality of life.
10 Natural Remedies for Incontinence

While medical treatment may be necessary for severe cases of urinary incontinence, there are some natural remedies that may help alleviate symptoms. Here are ten natural remedies for urinary incontinence:
- Kegel exercises: These exercises involve contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles, which can help improve bladder control.
- Bladder training: This involves setting a schedule for urination and gradually increasing the time between trips to the bathroom to help train the bladder to hold more urine.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help alleviate pressure on the bladder and reduce urinary incontinence symptoms.
- Avoiding bladder irritants: Certain foods and drinks, such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, can irritate the bladder and increase urinary incontinence symptoms.
- Magnesium supplementation: Magnesium may help relax the bladder muscles and reduce urinary incontinence symptoms.
- Herbal remedies: Some herbs, such as pumpkin seed extract, may help improve bladder control and reduce urinary incontinence symptoms.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to help improve bladder control.
- Yoga: Certain yoga poses, such as the bridge pose and the cobra pose, can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve bladder control.
- Biofeedback: This technique involves using sensors to monitor muscle activity in the pelvic floor muscles and using that feedback to learn how to better control those muscles.
- Mind-body techniques: Meditation, deep breathing, and visualization exercises can all help reduce stress and anxiety, which can contribute to urinary incontinence symptoms.

